linear static analysis of sheet metal parts In this post, we explored a wide range of FEA simulations—from linear and nonlinear static analysis to dynamic analysis with 2D simplification. Understanding the differences between these types of analysis will help you . $239.99
0 · Using Sheet Metal Bodies in SOLIDWORKS Simulation
1 · Structural Analysis with the Finite Element Method.
2 · Static Analysis of a Sheet Metal Part
3 · Static Analysis
4 · Solid Edge Simulation (FEA) Tutorials #6
5 · SOLIDWORKS Simulation Standard (FEA)
6 · Mastering FEA Simulation in SolidWorks: Linear,
7 · Linear Static Analysis: Meaning, Examples & Method
8 · Linear Static Analysis
9 · ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF SHEET
Using state-of-the-art technical weaving equipment, we create highly specialized architectural metal mesh systems in close cooperation with our clients to achieve the best results. Contact us today to see how we can support your design needs.
Using Sheet Metal Bodies in SOLIDWORKS Simulation
Linear Static Analysis is a method used in engineering to determine the responses of a structure under loading conditions. It assumes linearity in the relationships between force and displacement to efficiently predict .Linear Static analysis calculates displacements, strains, stresses, and reaction forces under the effect of applied loads. All loads are applied slowly and gradually until they reach their full .
This tutorial use linear static analysis to simulate the stresses on a sheet metal part. Sheet metal and other thin parts use a mid-surface as the study geom.
job duities for a lead painter at kmk metal fabricators
In this post, we explored a wide range of FEA simulations—from linear and nonlinear static analysis to dynamic analysis with 2D simplification. Understanding the differences between these types of analysis will help you . In this lesson, you learn the following: - Creating a static analysis study - Choosing a solver - Assigning material to the part - Applying a fixed restraint.Volume1 presents the basis of the FEM for structural analysis and a detailed description of the finite element formulation for axially loaded bars, plane elasticity problems, axisymmetric solids and general three dimensional solids.Linear Static analysis helps you to validate product performance and safety factors using finite element nalysis (FEA) to perform structural simulation. It is a primary tool to assess the displacement, strain and stress on parts and .
Two mesh refinement indicators based on the gradients of effective stresses (GSIG) and effective plastic strains (GEPS), respectively, are proposed for adaptive finite element analysis of the . In SimScale, Code Aster solver is used for performing static analysis. The results enable you to evaluate whether your component is deformed in an undesired manner or if a critical stress state occurs in your geometry.
Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: SimulationXpress: Sketching: SLDXML Data Exchange: SOLIDWORKS Sustainability: Tolerancing: . Linear Static analysis calculates displacements, strains, stresses, and reaction forces under the effect of applied loads. Linear static analysis makes the following assumptions:Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: Welcome to SolidWorks Simulation Online Help: Access to Help: Conventions: Legal Notices: . Linear Static Analysis. When loads are applied to a body, the body deforms and the effect of loads is transmitted throughout the body. The external loads induce internal forces and reactions to .
Linear Static analysis helps you to validate product performance and safety factors using finite element nalysis (FEA) to perform structural simulation. It is a primary tool to assess the displacement, strain and stress on parts and .Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.It is important to verify the static assumption since a dynamic load may generate stresses up to 1/(2x) times the stresses generated by static loads with the same magnitude, where x is the viscous damping ratio. For a lightly damped structure with 5% damping, the dynamic stresses will be 10 times larger than the static stresses.Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.
Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: Welcome to SOLIDWORKS Simulation Help: Accessing Help: Legal Notices: SOLIDWORKS Simulation Reference: . To perform linear static analysis, you need the following: Meshed model: You must mesh the model before running the analysis. Contact conditions must be defined before meshing.Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: SimulationXpress: Sketching: SOLIDWORKS MBD: SOLIDWORKS Utilities: SOLIDWORKS Sustainability: Tolerancing: . Linear Static analysis calculates displacements, strains, stresses, and reaction forces under the effect of applied loads. Linear static analysis makes the following assumptions:
In linear static analysis, the loads are applied gradually and slowly until they reach their full magnitude. After reaching their full magnitude, the loads remain constant (time-invariant). The accelerations and velocities of the excited system are negligible, therefore, no inertial and damping forces are considered in the formulation:
Linear and Nonlinear Static Analysis. . Assign Alloy Steel to all parts. . Run the simulation and observe the stress, strain, and displacement values on the sheet metal as the punch moves downward. Interpreting the Results . Once the simulation is complete, you'll be able to visualize the deformation, stress, .
Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: SimulationXpress: Sketching: SLDXML Data Exchange: SOLIDWORKS Sustainability: Tolerancing: . Linear Static analysis calculates displacements, strains, stresses, and reaction forces under the effect of applied loads. Linear static analysis makes the following assumptions:Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.
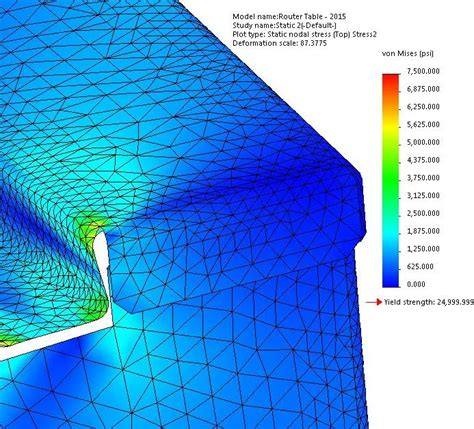
Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.In linear static analysis, the loads are applied gradually and slowly until they reach their full magnitude. After reaching their full magnitude, the loads remain constant (time-invariant). The accelerations and velocities of the excited system are negligible, therefore, no inertial and damping forces are considered in the formulation:Linear static analysis assumes that the relationship between loads and the induced response is _____. Linear. In SOLIDWORKS Simulation, the Factor of Safety (FOS) calculations are based on one of the following failure criterion.
Linear static analysis assumes that the relationship between loads and the induced response is: linear. In SOLIDWORKS Simulation, the Factor of Safety (FOS) calculations for tensile materials are based on one or more of the following failure criteria.Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: Welcome to SOLIDWORKS Simulation Help: Accessing and Using Help: Legal Notices: SOLIDWORKS Simulation Reference: SOLIDWORKS Simulation Fundamentals: Analysis Background: Linear Static Analysis: Frequency Analysis: Dynamic Analysis: Linearized Buckling Analysis: Thermal Analysis:
Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: Welcome to SOLIDWORKS Simulation Help: Accessing Help: Legal Notices: SOLIDWORKS Simulation Reference: . To perform linear static analysis, you need the following: Meshed model: You must mesh the model before running the analysis. Contact conditions must be defined before meshing.When to Use Nonlinear Analysis. Structural Nonlinearities. Solution Procedures for Nonlinear Problems. Nonlinear Dynamic Studies. Numerical Procedures. Result Options PropertyManager. The Result Options PropertyManager allows you to set result options for static, linear dynamic, nonlinear studies, and thermal transient studies. Performing .
In some cases, linear analysis may be adequate. In many other cases, the linear solution can produce erroneous results because the assumptions upon which it is based are violated. Nonlinearity can be caused by the material behavior, large displacements, and contact conditions. You can use a nonlinear study to solve a linear problem.Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.
Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.
Parts and Features: PhotoView 360: PhotoWorks: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: Welcome to SolidWorks Simulation Online Help: Access to Help: Conventions: Legal Notices: Analysis Background: SolidWorks Simulation Reference: . Linear Static analysis calculates displacements, strains, stresses, and reaction forces under the effect of applied .Parts and Features: Routing: Sheet Metal: Simulation: Welcome to SOLIDWORKS Simulation Help: Accessing Help: Legal Notices: . Output of Linear Static Analysis. By default, directions X, Y, and Z refer to the global coordinate system. If you choose a reference geometry, these directions refer to the selected reference entity. .Please refer to the section of Dynamic Analysis. You can use static analysis to calculate the structural response of bodies spinning with constant velocities or traveling with constant accelerations since the generated loads do not change with time. Use linear or nonlinear dynamic studies to calculate the structural response due to dynamic loads.

joanns fabric metal rings
$9.99
linear static analysis of sheet metal parts|ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF SHEET